Template Annotations
This topic describes how to use Replicated template functions to template annotations for resources and objects based on user-supplied values.
Overview
It is common for users to need to set custom annotations for a resource or object deployed by your application. For example, you might need to allow your users to provide annotations to apply to a Service or Ingress object in public cloud environments.
For applications installed with Replicated KOTS, you can apply user-supplied annotations to resources or objects by first adding a field to the Replicated Admin Console Config page where users can enter one or more annotations. For information about how to add fields on the Config page, see Create and Edit Configuration Fields.
You can then map these user-supplied values from the Config page to resources and objects in your release using Replicated template functions. Replicated template functions are a set of custom template functions based on the Go text/template library that can be used to generate values specific to customer environments. The template functions in the Config context return user-supplied values on the Config page.
For more information about Replicated template functions in the Config text, see Config Context. For more information about the Go library, see text/template in the Go documentation.
About kots.io/placeholder
For applications installed with KOTS that use standard Kubernetes manifests, the kots.io/placeholder annotation allows you to template annotations in resources and objects without breaking the base YAML or needing to include the annotation key.
The kots.io/placeholder annotation uses the format kots.io/placeholder 'bool' 'string'. For example:
# Example manifest file
annotations:
kots.io/placeholder: |-
repl{{ ConfigOption "additional_annotations" | nindent 4 }}
For Helm chart-based applications installed with KOTS, Replicated recommends that you map user-supplied annotations to the Helm chart values.yaml file using the Replicated HelmChart custom resource, rather than using kots.io/placeholder. This allows you to access user-supplied values in your Helm chart without needing to include Replicated template functions directly in the Helm chart templates.
For an example, see Map User-Supplied Annotations to Helm Chart Values below.
Annotation Templating Examples
This section includes common examples of templating annotations in resources and objects to map user-supplied values.
For additional examples of how to map values to Helm chart-based applications, see Applications in the platform-examples repository in GitHub.
Map Multiple Annotations from a Single Configuration Field
You can map one or more annotations from a single textarea field on the Config page. The textarea type defines multi-line text input and supports properties such as rows and cols. For more information, see textarea in Config.
For example, the following Config custom resource adds an ingress_annotations field of type textarea:
# Config custom resource
apiVersion: kots.io/v1beta1
kind: Config
metadata:
name: config
spec:
groups:
- name: ingress_settings
title: Ingress Settings
description: Configure Ingress
items:
- name: ingress_annotations
type: textarea
title: Ingress Annotations
help_text: See your cloud provider’s documentation for the required annotations.
On the Config page, users can enter one or more key value pairs in the ingress_annotations field, as shown in the example below:
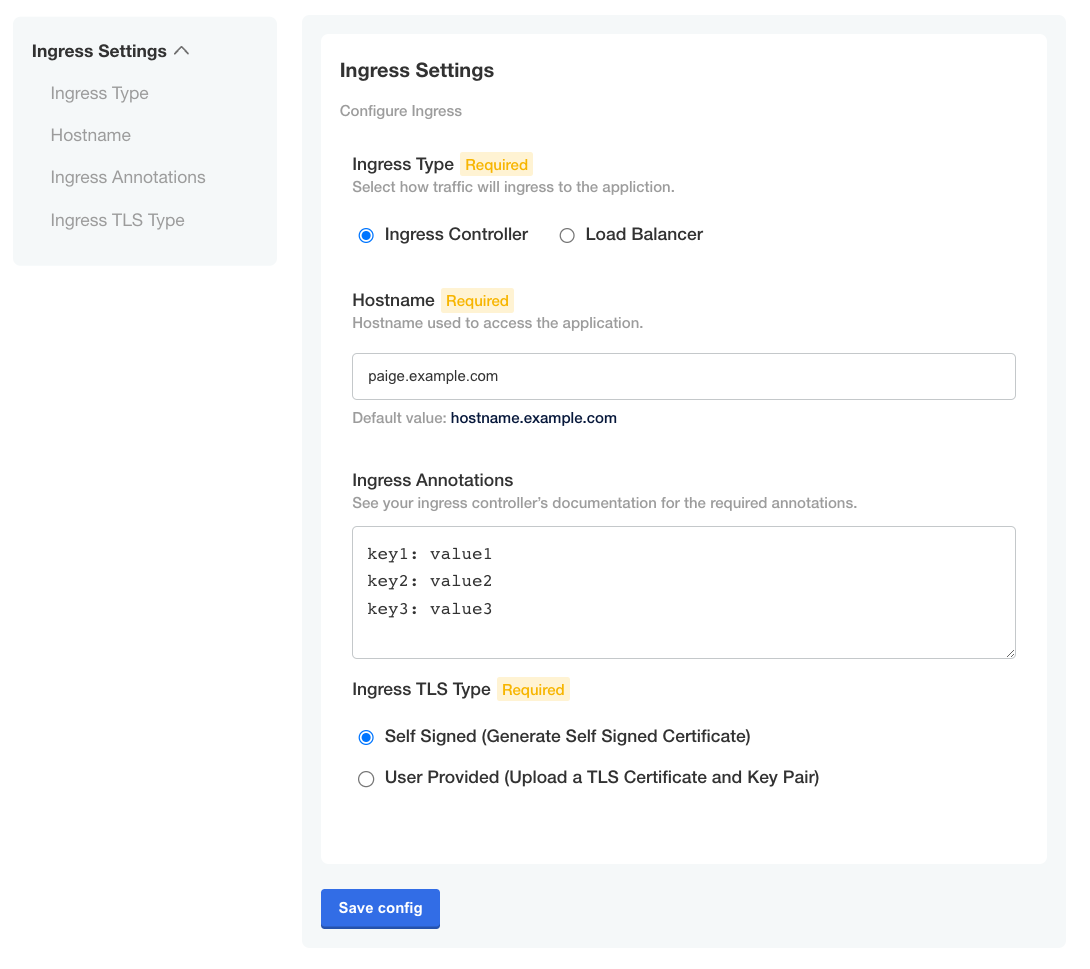
View a larger version of this image
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: example-annotation
annotations:
kots.io/placeholder: |-
repl{{ ConfigOption "ingress_annotations" | nindent 4 }}
During installation, KOTS renders the YAML with the multi-line input from the configuration field as shown below:
# Rendered Ingress object
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: example-annotation
annotations:
kots.io/placeholder: |-
key1: value1
key2: value2
key3: value3
Map Annotations from Multiple Configuration Fields
You can specify multiple annotations using the same kots.io/placeholder annotation.
For example, the following Ingress object includes ConfigOption template functions that render the user-supplied values for the ingress_annotation and ingress_hostname fields:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: example-annotation
annotations:
kots.io/placeholder: |-
repl{{ ConfigOption "ingress_annotation" | nindent 4 }}
repl{{ printf "my.custom/annotation.ingress.hostname: %s" (ConfigOption "ingress_hostname") | nindent 4 }}
During installation, KOTS renders the YAML as shown below:
# Rendered Ingress object
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: example-annotation
annotations:
kots.io/placeholder: |-
key1: value1
my.custom/annotation.ingress.hostname: example.hostname.com
Map User-Supplied Value to a Key
You can map a user-supplied value from the Config page to a pre-defined annotation key.
For example, in the following Ingress object, my.custom/annotation.ingress.hostname is the key for the templated annotation. The annotation also uses the ConfigOption template function to map the user-supplied value from a ingress_hostname configuration field:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: example-annotation
annotations:
kots.io/placeholder: |-
repl{{ printf "my.custom/annotation.ingress.hostname: %s" (ConfigOption "ingress_hostname") | nindent 4 }}
During installation, KOTS renders the YAML as shown below:
# Rendered Ingress object
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: example-annotation
annotations:
kots.io/placeholder: |-
my.custom/annotation.ingress.hostname: example.hostname.com
Include Conditional Statements in Templated Annotations
You can include or exclude templated annotations based on a conditional statement.
For example, the following Ingress object includes a conditional statement for kots.io/placeholder that renders my.custom/annotation.class: somevalue if the user enables a custom_annotation field on the Config page:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: myapp
labels:
app: myapp
annotations:
kots.io/placeholder: |-
repl{{if ConfigOptionEquals "custom_annotation" "1" }}repl{{ printf "my.custom/annotation.class: somevalue" | nindent 4 }}repl{{end}}
spec:
...
During installation, if the user enables the custom_annotation configuration field, KOTS renders the YAML as shown below:
# Rendered Ingress object
apiVersion: v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: myapp
labels:
app: myapp
annotations:
kots.io/placeholder: |-
my.custom/annotation.class: somevalue
spec:
...
Alternatively, if the condition evaluates to false, the annotation does not appear in the rendered YAML:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: myapp
labels:
app: myapp
annotations:
kots.io/placeholder: |-
spec:
...
Map User-Supplied Annotations to Helm Chart Values
For Helm chart-based applications installed with KOTS, Replicated recommends that you map user-supplied annotations to the Helm chart values.yaml file, rather than using kots.io/placeholder. This allows you to access user-supplied values in your Helm chart without needing to include Replicated template functions directly in the Helm chart templates.
To map user-supplied annotations from the Config page to the Helm chart values.yaml file, you use the values field of the Replicated HelmChart custom resource. For more information, see values in HelmChart v2.
For example, the following HelmChart custom resource uses a ConfigOption template function in values.services.myservice.annotations to map the value of a configuration field named additional_annotations:
# HelmChart custom resource
apiVersion: kots.io/v1beta2
kind: HelmChart
metadata:
name: myapp
spec:
values:
services:
myservice:
annotations: repl{{ ConfigOption "additional_annotations" | nindent 10 }}
The values.services.myservice.annotations field in the HelmChart custom resource corresponds to a services.myservice.annotations field in the value.yaml file of the application Helm chart, as shown in the example below:
# Helm chart values.yaml
services:
myservice:
annotations: {}
During installation, the ConfigOption template function in the HelmChart custom resource renders the user-supplied values from the additional_annotations configuration field.
Then, KOTS replaces the value in the corresponding field in the values.yaml in the chart archive, as shown in the example below.
# Rendered Helm chart values.yaml
services:
myservice:
annotations:
key1: value1
In your Helm chart templates, you can access these values from the values.yaml file to apply the user-supplied annotations to the target resources or objects. For information about how to access values from a values.yaml file, see Values Files in the Helm documentation.