About Preflight Checks and Support Bundles
This topic provides an introduction to preflight checks and support bundles, which are provided by the Troubleshoot open source project.
For more information, see the Troubleshoot documentation.
Overview
Preflight checks and support bundles are provided by the Troubleshoot open source project, which is maintained by Replicated. Troubleshoot is a kubectl plugin that provides diagnostic tools for Kubernetes applications. For more information, see the open source Troubleshoot documentation.
Preflight checks and support bundles analyze data from customer environments to provide insights that help users to avoid or troubleshoot common issues with an application:
- Preflight checks run before an application is installed to check that the customer environment meets the application requirements.
- Support bundles collect troubleshooting data from customer environments to help users diagnose problems with application deployments.
Preflight checks and support bundles consist of collectors, redactors, and analyzers that are defined in a YAML specification. When preflight checks or support bundles are executed, data is collected, redacted, then analyzed to provide insights to users, as illustrated in the following diagram:

View a larger version of this image
For more information about each step in this workflow, see the sections below.
Collect
During the collection phase, collectors gather information from the cluster, the environment, the application, and other sources.
The data collected depends on the types of collectors that are included in the preflight or support bundle specification. For example, the Troubleshoot project provides collectors that can gather information about the Kubernetes version that is running in the cluster, information about database servers, logs from pods, and more.
For more information, see the Collect section in the Troubleshoot documentation.
Redact
During the redact phase, redactors censor sensitive customer information from the data before analysis. By default, the following information is automatically redacted:
- Passwords
- API token environment variables in JSON
- AWS credentials
- Database connection strings
- URLs that include usernames and passwords
For Replicated KOTS and Embedded Cluster installations, it is also possible to add custom redactors to redact additional data. For more information, see the Redact section in the Troubleshoot documentation.
Analyze
During the analyze phase, analyzers use the redacted data to provide insights to users.
For preflight checks, analyzers define the pass, fail, and warning outcomes, and can also display custom messages to the user. For example, you can define a preflight check that fails if the cluster's Kubernetes version does not meet the minimum version that your application supports.
For support bundles, analyzers can be used to identify potential problems and share relevant troubleshooting guidance with users. Additionally, when a support bundle is uploaded to the Vendor Portal, it is extracted and automatically analyzed. The goal of analyzers in support bundles is to surface known issues or hints of what might be a problem to make troubleshooting easier.
For more information, see the Analyze section in the Troubleshoot documentation.
Preflight Checks
This section provides an overview of preflight checks, including how preflights are defined and run.
Overview
Preflight checks let you define requirements for the cluster where your application is installed. When run, preflight checks provide clear feedback to your customer about any missing requirements or incompatibilities in the cluster before they install or upgrade your application. For KOTS installations, preflight checks can also be used to block the deployment of the application if one or more requirements are not met.
Thorough preflight checks provide increased confidence that an installation or upgrade will succeed and help prevent support escalations.
About Host Preflights
Host preflight checks automatically run during Replicated Embedded Cluster and Replicated kURL installations on a VM or bare metal server. The purpose of host preflight checks is to verify that the user's installation environment meets the requirements of the Embedded Cluster or kURL installer, such as checking the number of CPU cores in the system, available disk space, and memory usage. If any of the host preflight checks fail, installation is blocked and a message describing the failure is displayed.
Host preflight checks are separate from any application-specific preflight checks that are defined in the release, which run in the Admin Console before the application is deployed with KOTS. Both Embedded Cluster and kURL have default host preflight checks that are specific to the requirements of the given installer. For kURL installations, it is possible to customize the default host preflight checks.
For more information about the default Embedded Cluster host preflight checks, see Host Preflight Checks in Using Embedded Cluster.
For more information about kURL host preflight checks, including information about how to customize the defaults, see Customize Host Preflight Checks for kURL.
Defining Preflights
To add preflight checks for your application, create a Preflight YAML specification that defines the collectors and analyzers that you want to include.
For information about how to add preflight checks to your application, including examples, see Define Preflight Checks.
Blocking Installation with Required (Strict) Preflights
For applications installed with KOTS or Embedded Cluster, it is possible to block the deployment of a release if a preflight check fails. This is helpful when it is necessary to prevent an installation or upgrade from continuing unless a given requirement is met.
You can add required preflight checks for an application by including strict: true for the target analyzer in the preflight specification. For more information, see Block Installation with Required (Strict) Preflights in Define Preflight Checks.
Running Preflights
This section describes how users can run preflight checks for KOTS and Helm installations.
Replicated Installations
For Replicated installations with Embedded Cluster, KOTS, or kURL, preflight checks run automatically as part of the installation process. The results of the preflight checks are displayed either in the KOTS Admin Console or in the KOTS CLI, depending on the installation method.
Additionally, users can access preflight checks from the Admin Console after installation to view their results and optionally re-run the checks.
The following shows an example of the results of preflight checks displayed in the Admin Console during installation:
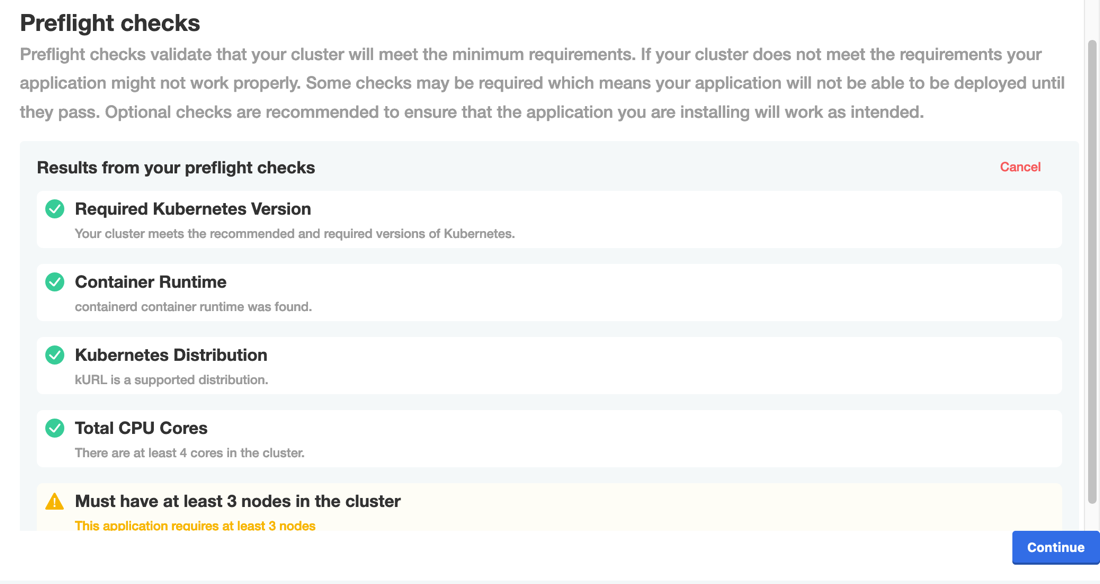
View a larger version of this image
Helm Installations
For installations with Helm, the preflight kubectl plugin is required to run preflight checks. The preflight plugin is a client-side utility that adds a single binary to the path. For more information, see Getting Started in the Troubleshoot documentation.
Users can optionally run preflight checks before they run helm install. The results of the preflight checks are then displayed through the CLI, as shown in the example below:
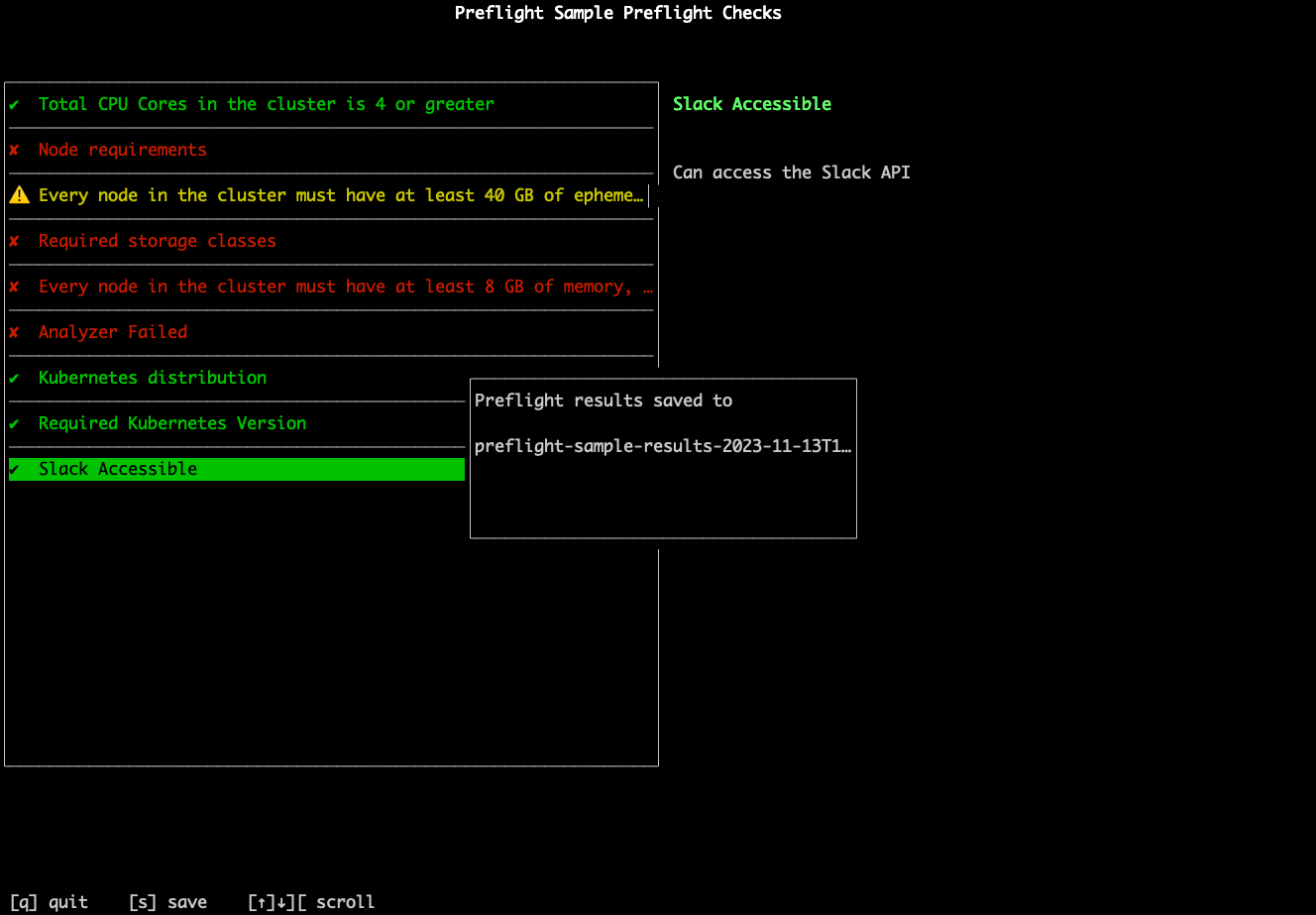
View a larger version of this image
For more information, see Run Preflight Checks for Helm Installations.
Support Bundles
This section provides an overview of support bundles, including how support bundles are customized and generated.
Overview
A support bundle is a diagnostic tool that collects and analyzes key troubleshooting data from a customer deployment. Support bundles are designed to help end customers self-diagnose and resolve issues.
When it is necessary for the customer to escalate their issue, support bundles provide vendor support teams with the information they need for troubleshooting upfront, reducing overall issue resolution time. Replicated has found that Severity 1 issues are resolved three times faster when a support bundle is provided during an issue escalation.
The data collected in a support bundle depends on the collectors and redactors defined by the vendor in the support bundle spec included with the application release. For more information about the automatic redactions that are made in support bundles, see Redact above. For more information about customizing the data that is collected in support bundles for your application, see Customizing the Support Bundle Spec For Your Application below.
When an end customer generates a support bundle, the process uses the vendor-defined spec to collect data from the cluster, redact sensitive fields, and then perform an analysis on the data to provide remediation steps. The output is a compressed tar.gz file that can be shared with the vendor as part of a support escalation. For more information, see How Customers Generate and Share Support Bundles below.
No data is shared outside the cluster unless the tar.gz support bundle file is explicitly shared by the end customer.
The following diagram demonstrates how end customers can generate support bundles in their installation environment, then upload the bundle to the Enterprise Portal and share it with the vendor. It also shows how, after a support bundle is uploaded and shared, vendors can inspect the bundle from the Vendor Portal Support bundle analysis page.
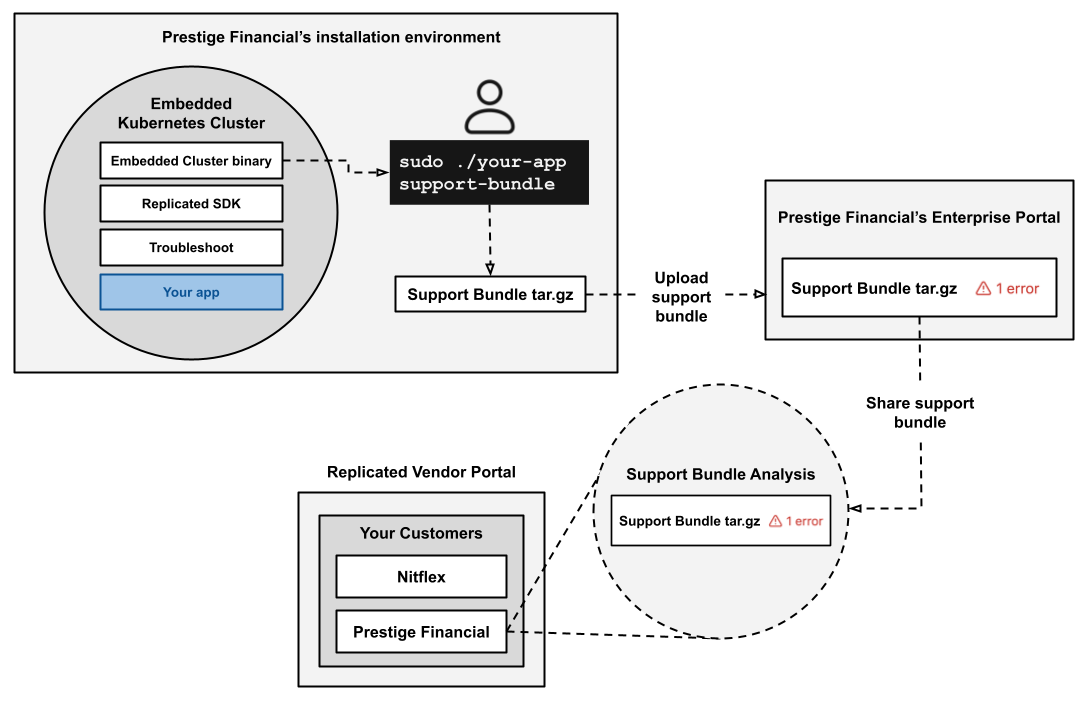
View a larger version of this image
About Host Support Bundles
For installations on VMs or bare metal servers with Replicated Embedded Cluster or Replicated kURL, it is possible to generate a support bundle that includes host-level information to help troubleshoot failures related to host configuration like DNS, networking, or storage problems.
For Embedded Cluster installations, a default spec can be used to generate support bundles that include cluster- and host-level information. See Generate Host Bundles for Embedded Cluster.
For kURL installations, vendors can customize a host support bundle spec for their application. See Generate Host Bundles for kURL.
Customizing the Support Bundle Spec For Your Application
To enable customers to collect support bundles for your application, add a support bundle YAML specification to an application release. An empty support bundle specification automatically includes default redactors, as well as several default collectors and analzyers. You can also optionally customize the support bundle specification by adding, removing, or editing collectors and analyzers.
Support bundles can collect a variety of important cluster-level data from customer environments, such as:
- Pod logs
- Node resources and status
- The status of replicas in a Deployment
- Cluster information
- Resources deployed to the cluster
- The history of Helm releases installed in the cluster
Support bundles can also be used for more advanced use cases, such as checking that a command successfully executes in a pod in the cluster, or that an HTTP request returns a succesful response.
For more information, see Add and Customize Support Bundles.
How Customers Generate and Share Support Bundles
Users generate support bundles as tar.gz files from the command line using the support-bundle kubectl plugin. KOTS and Embedded Cluster users can also generate bundles from the Admin Console UI.
Your customers can share their support bundles with your team by sending you the tar.gz file. No data is shared outside the cluster unless the tar.gz support bundle file is explicitly shared by the end customer.
Replicated recommends that customers share their support bundles with you using one of the following methods:
- Upload the support bundle in their Enterprise Portal. This allows the customer to download and delete their own support bundles. For more information, see Collect, Upload, and Manage Support Bundles in Access and Use the Enterprise Portal.
- KOTS and Embedded Cluster users can also generate and share support bundles from the Admin Console. For more information, see Generate Support Bundles from the Admin Console.
When customers upload their support bundle in the Enterprise Portal or Admin Console, the support bundle and its comprehensive analysis results are automatically made available to you in the Vendor Portal.
Managing and Inspecting Support Bundles in the Vendor Portal
Support bundles are automatically uploaded to the Vendor Portal when customers share bundles through the Enterprise Portal or Admin Console. You can also manually upload support bundle .tar.gz files to the Vendor Portal.
From the Vendor Portal, you have control over uploaded support bundles, including sharing bundles with Replicated or deleting previously uploaded bundles. Support bundles uploaded to the Vendor Portal are stored per Replicated's data and security standards. For more information, see Security at Replicated.
You can inspect uploaded support bundles on the Vendor Portal Support bundle analysis page:
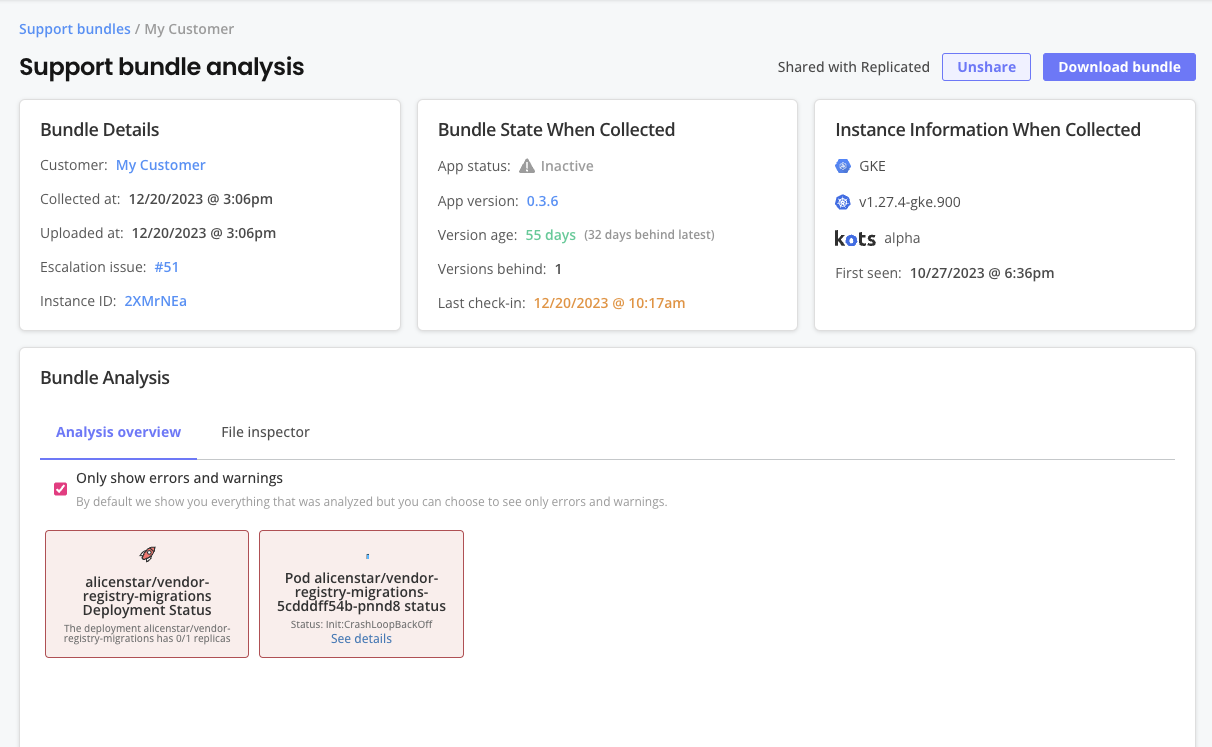
View a larger version of this image
As shown in the image above, the Support bundle analysis page includes information and features to help you analyze a support bundle, such as:
- Details about the bundle, including the customer and instance it is associated with, when it was collected and uploaded, and more
- Any available instance details from the point in time when the bundle was collected
- An analysis overview that can be filtered to show errors and warnings
- A file inspector for more detailed analaysis
From the Support bundle analysis page, you can also share the bundle with Replicated or download the bundle for offline analysis.
For more information about using the Support bundle analysis page, see Inspect Support Bundles.
Sharing Support Bundles with Replicated
Replicated strongly recommends that you always provide a support bundle when you open a new support request, and that you attach new bundles to an existing support issue when conditions change or new problems arise. Sharing an existing support bundle or uploading a new one is secure and provides the Replicated Support team immediate access to necessary diagnostic data, enabling them to provide faster and more informed assistance in troubleshooting your application.
For more information, see Submit a Support Request.