Replicated FAQs
This topic lists frequently-asked questions (FAQs) for different components of the Replicated Platform.
Getting Started FAQs
What are the supported application packaging options?
Replicated strongly recommends that all applications are packaged using Helm.
Helm is a popular open source package manager for Kubernetes applications. Many ISVs use Helm to configure and deploy Kubernetes applications because it provides a consistent, reusable, and sharable packaging format. For more information, see the Helm documentation.
Many enterprise customers expect to be able to install an application with Helm in their own cluster. Packaging with Helm allows you to support installation with the Helm CLI and with the Replicated installers (Replicated Emebdded Cluster and Replicated KOTS) from a single release in the Replicated Platform.
For vendors that do not want to use Helm, applications distributed with Replicated can be packaged as Kubernetes manifest files.
How do I get started with Replicated?
Replicated recommends that new users start by completing our Quick Start tutorial. You can also complete one or more of the following labs to get familiar with the processes of creating, installing, and iterating on releases for an application with the Replicated Platform:
- Distributing Your Application with Replicated: Learn how to quickly get value from the Replicated Platform for your application.
- Delivering Your Application as a Kubernetes Appliance: Use Embedded Cluster to distribute Kubernetes and an application together as a single appliance.
- Avoiding Installation Pitfalls: Learn how to use preflight checks to avoid common installation issues and assure your customer is installing into a supported environment.
- Closing the Support Information Gap: Learn how to use support bundles to close the information gap between your customers and your support team.
- Protecting Your Assets: Assure your customers have the right access to your application artifacts and features using Replicated licensing.
Then, when you are ready to begin onboarding your own application to the Replicated Platform, see Onboard to the Replicated Platform for a list of Replicated features to begin integrating.
What are air gap installations?
Air gap refers to a computer or network that does not have outbound internet access. Air-gapped environments are common for enterprises that require high security, such as government agencies or financial institutions.
Traditionally, air-gapped systems are physically isolated from the network. For example, an air-gapped server might be stored in a separate location away from network-connected servers. Physical access to air-gapped servers is often restricted as well.
It is also possible to use virtual or logical air gaps, in which security controls such as firewalls, role-based access control (RBAC), and encryption are used to logically isolate a device from a network. In this way, network access is still restricted, but there is not a phyiscal air gap that disconnects the device from the network.
Replicated supports installations into air-gapped environments. In an air gap installation, users first download the images and other assets required for installation on an internet-connected device. These installation assets are usually provided in an air gap bundle that ISVs can build in the Replicated Vendor Portal. Then, users transfer the installation assets to their air-gapped machine where they can push the images to an internal private registry and install.
For more information, see:
- Air Gap Installation with Embedded Cluster
- Installing and Updating with Helm in Air Gap Environments
What is the Commercial Sotware Distribution Lifecycle?
Commercial software distribution is the business process that independent software vendors (ISVs) use to enable enterprise customers to self-host a fully private instance of the vendor's application in an environment controlled by the customer.
Replicated has developed the Commercial Software Distribution Lifecycle to represent the stages that are essential for every company that wants to deliver their software securely and reliably to customer-controlled environments.
This lifecycle was inspired by the DevOps lifecycle and the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC), but it focuses on the unique things requirements for successfully distributing commercial software to tens, hundreds, or thousands of enterprise customers.
The phases are:
- Develop
- Test
- Release
- License
- Install
- Report
- Support
For more information about the Replicated features that enhance each phase of the lifecycle, see Introduction to Replicated.
Compatibility Matrix FAQs
What types of clusters can I create with Compatibility Matrix?
You can use Compatibility Matrix (CMX) to get kubectl access to running clusters within minutes or less. CMX supports a variety of VM and cloud distributions, including Red Hat OpenShift, Replicated Embedded Cluster, and Oracle Container Engine for Kubernetes (OKE). For a complete list, see CMX Cluster and VM Types.
How does billing work?
Clusters created with CMX are billed by the minute. Per-minute billing begins when the cluster reaches a running status and ends when the cluster is deleted. For more information, see Billing and Credits.
How do I buy credits?
To create clusters with CMX, you must have credits in your Vendor Portal account. If you have a contract, you can purchase credits by logging in to the Vendor Portal and going to Compatibility Matrix > Buy additional credits. Otherwise, to request credits, log in to the Vendor Portal and go to Compatibility Matrix > Request more credits.
How do I add Comaptibility Matrix to my CI/CD pipelines?
You can use Replicated CLI commands to integrate CMX into your CI/CD development and production workflows. This allows you to programmatically create multiple different types of clusters where you can deploy and test your application before releasing.
For more information, see About Integrating with CI/CD.
KOTS and Embedded Cluster FAQs
What is the Admin Console?
The Admin Console is the user interface deployed by the Replicated KOTS installer. Users log in to the Admin Console to configure and install the application. Users also access to the Admin Console after installation to complete application mangement tasks such as performing updates, syncing their license, and generating support bundles. For installations with Embedded Cluster, the Admin Console also includes a Cluster Management tab where users can manage the nodes in the cluster.
The Admin Console is available in installations with Replicated Embedded Cluster and Replicated KOTS.
The following shows an example of the Admin Console dashboard for an Embedded Cluster installation of an application named "Gitea":
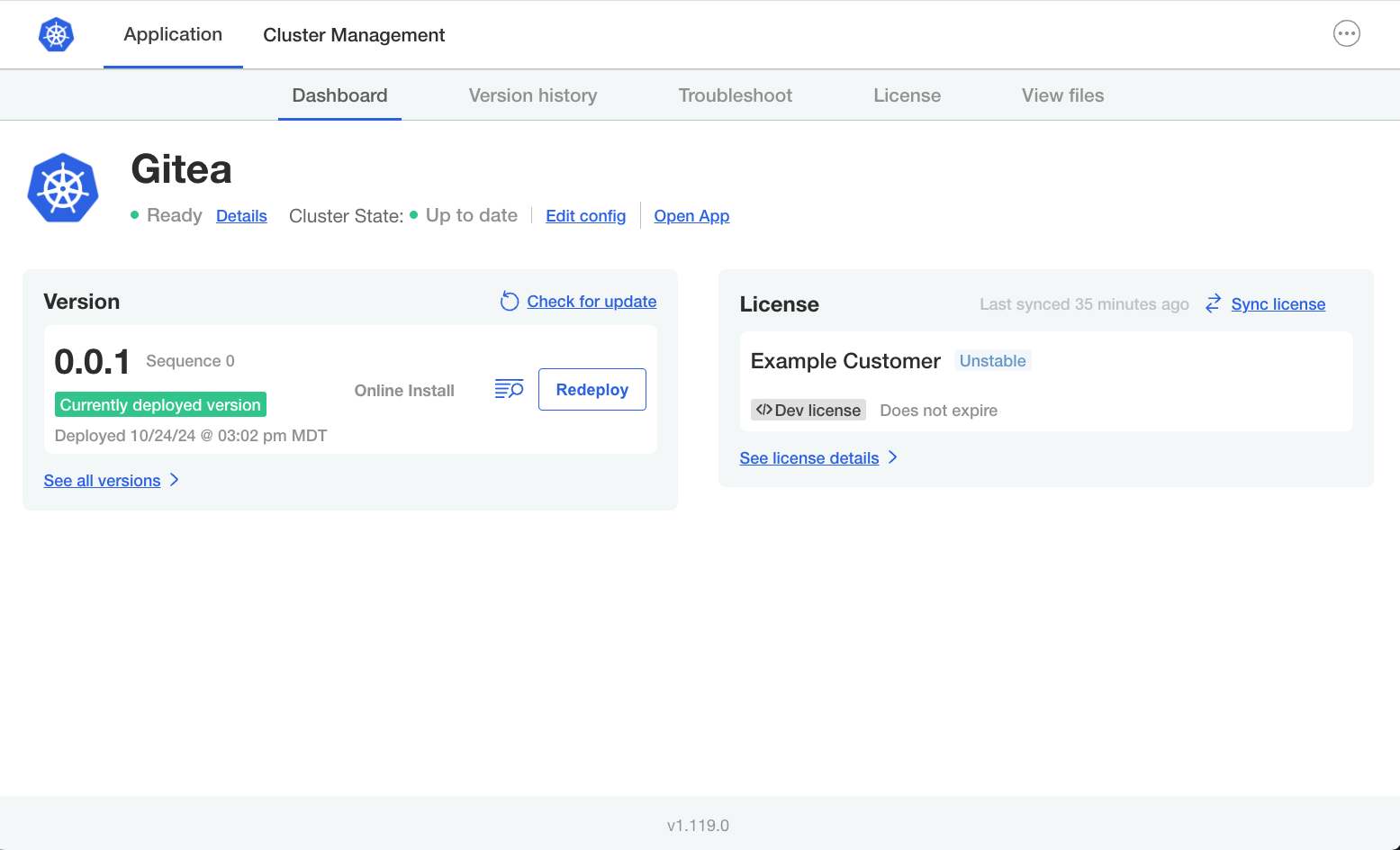
View a larger version of this image
How do Embedded Cluster installations work?
To install with Embedded Cluster, users first download and extract the Embedded Cluster installation assets for the target application release on their VM or bare metal server. Then, they run an Embedded Cluster installation command to provision the cluster. During installation, Embedded Cluster also installs Replicated KOTS in the cluster, which deploys the Admin Console.
After the installation command finishes, users log in to the Admin Console to provide application configuration values, optionally join more nodes to the cluster, run preflight checks, and deploy the application.
Customer-specific Embedded Cluster installation instructions are provided in the Replicated Vendor Portal. For more information, see Install with Embedded Cluster.
Does Replicated support installations into air gap environments?
Yes. The Embedded Cluster and KOTS installers support installation in air gap environments with no outbound internet access.
To support air gap installations, vendors can build air gap bundles for their application in the Vendor Portal that contain all the required assets for a specific release of the application. Additionally, Replicated provides bundles that contain the assets for the Replicated installers.
For more information about how to install with Embedded Cluster and KOTS in air gap environments, see Air Gap Installation with Embedded Cluster and Air Gap Installation in Existing Clusters with KOTS.
Can I deploy Helm charts with KOTS?
Yes. An application deployed with KOTS can use one or more Helm charts, can include Helm charts as components, and can use more than a single instance of any Helm chart. Each Helm chart requires a unique HelmChart custom resource (apiVersion: kots.io/v1beta2) in the release.
For more information, see About Distributing Helm Charts with KOTS.
What's the difference between Embedded Cluster and kURL?
Replicated Embedded Cluster is a successor to Replicated kURL. Compared to kURL, Embedded Cluster feature offers significantly faster installation, updates, and node joins, a redesigned Admin Console UI, improved support for multi-node clusters, one-click updates that update the application and the cluster at the same time, and more.
Replicated kURL is available only for existing customers. If you are not an existing kURL user, use Replicated Embedded Cluster instead. For more information, see Use Embedded Cluster.
kURL is a Generally Available (GA) product for existing customers. For more information about the Replicated product lifecycle phases, see Support Lifecycle Policy.
For more information, see Embedded Cluster Overview.
How do I enable Embedded Cluster and KOTS installations for my application?
Releases that support installation with KOTS include the manifests required by KOTS to define the Admin Console experience and install the application.
In addition to the KOTS manifests, releases that support installation with Embedded Cluster also include the Embedded Cluster Config. The Embedded Cluster Config defines aspects of the cluster that will be provisioned and also sets the version of KOTS that will be installed.
For more information, see Embedded Cluster Overview.
Can I use my own branding?
The KOTS Admin Console and the Replicated Download Portal support the use of a custom logo. Additionally, software vendors can use custom domains to alias the endpoints for Replicated services.
For more information, see Customize the Admin Console and Download Portal and About Custom Domains.
For more information, see Use Custom Domains.
Replicated SDK FAQs
What is the SDK?
The Replicated SDK is a Helm chart that can be installed as a small service alongside your application. You can distribute the Replicated SDK with your application by including it as a dependency of your parent Helm chart.
The Replicated SDK provides access to insights and operational telemetry for instances running in customer environments. You can use the Replicated SDK's in-cluster API to integrate key Replicated functionality with your application. For example:
- Collect custom metrics on instances running in online or air gap environments. See Configure Custom Metrics.
- Check customer license entitlements. See Query Entitlements with the Replicated SDK API and Verify License Field Signatures with the Replicated SDK API.
- Provide update checks to alert customers when new versions of your application are available for upgrade. See Support Update Checks in Your Application in Replicated SDK API.
- Programmatically name or tag instances from the instance itself. See Programatically Set Tags.
Is the SDK supported in air gap environments?
Yes. The Replicated SDK has an air gap mode that allows it to run in environments with no outbound internet access. When installed in air gap mode, the SDK does not attempt to connect to the internet. This avoids any failures that would occur when the SDK is unable to make outbound requests in air gap environments.
For more information, see Install the SDK in Air Gap Environments.
How do I develop against the SDK API?
You can use the Replicated SDK in integration mode to develop locally against the SDK API without needing to make real changes in the Replicated Vendor Portal or in your environment.
For more information, see Develop Against the SDK API.
How does the Replicated SDK work with KOTS?
The Replicated SDK is a Helm chart that can be installed as a small service alongside an application, or as a standalone component. The SDK can be installed using the Helm CLI or KOTS.
Replicated recommends that all applications include the SDK because it provides access to key functionality not available through KOTS, such as support for sending custom metrics from application instances. When both the SDK and KOTS are installed in a cluster alongside an application, both send instance telemetry to the Vendor Portal.
For more information about the SDK installation options, see Install the Replicated SDK.
Vendor Portal FAQs
How do I add and remove team members?
Admins can add, remove, and manage team members from the Vendor Portal. For more information, see Manage Team Members.
How do I manage RBAC policies for my team members?
By default, every team has two policies created automatically: Admin and Read Only. If you have an Enterprise plan, you will also have the Sales and Support policies created automatically. These default policies are not configurable.
You can also configure custom RBAC policies if you are on the Enterprise pricing plan. Creating custom RBAC policies lets you limit which areas of the Vendor Portal are accessible to team members, and control read and read/write privileges to groups based on their role.
For more information, see Configure RBAC Policies.
Can I alias Replicated endpoints?
Yes. Replicated supports the use of custom domains to alias the endpoints for Replicated services, such as the Replicated app service and the Replicated proxy registry.
Replicated domains are external to your domain and can require additional security reviews by your customer. Using custom domains as aliases can bring the domains inside an existing security review and reduce your exposure.
For more information, see Use Custom Domains.
How does Replicated collect telemetry from instances of my application?
For instances running in online (internet-connected) customer environments, either Replicated KOTS or the Replicated SDK periodically sends a small amount of data to the Vendor Portal, depending on which is installed in the cluster alongside the application. If both KOTS and the SDK are installed in the cluster, then both send instance data.
For air gap instances, Replicated KOTS and the Replicated SDK collect and store instance telemetry in a Kubernetes Secret in the customer environment. The telemetry stored in the Secret is collected when a support bundle is generated in the environment. When the support bundle is uploaded to the Vendor Portal, the telemetry is associated with the correct customer and instance ID, and the Vendor Portal updates the instance insights and event data accordingly.
For more information, see About Instance and Event Data.