Collect and View Network Reports
This topic describes how to enable and view network reports for environments created with Replicated Compatibility Matrix (CMX).
About Network Reports
CMX network reporting helps you understand your application's network activity. To provide flexibility in testing, you can enable network reporting to capture all network activity, whether the network policy is set to open or airgap.
Even when the network policy is set to airgap and network egress is blocked, all connection attempts and DNS queries are still captured in the report. This helps you identify unexpected network calls before deploying to an air-gapped environment.
For more information about working with CMX networks, see Create Air-Gapped Environments (Beta) and Create Environments on the Same Network in Create and Manage Environments
Types of Network Reports
The following tables describes the CMX network report types:
| Report Type | Description | Report Contents |
|---|---|---|
| Running Report | See all network events captured in near real-time |
|
| Report Summary | Aggregated analysis of captured network events |
|
The following shows an example of a running report:
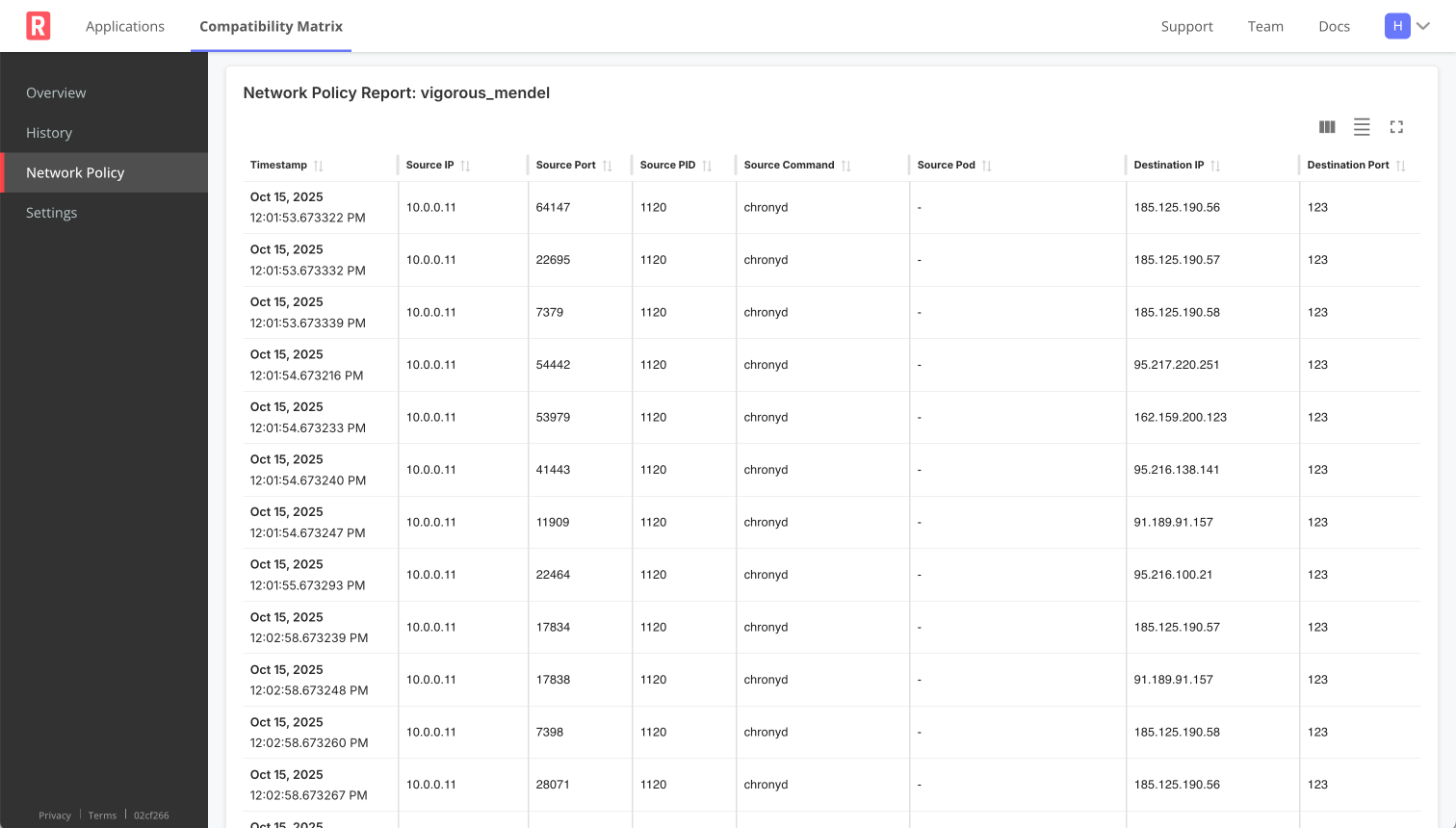
View a larger version of this image
The following shows an example of a report summary:
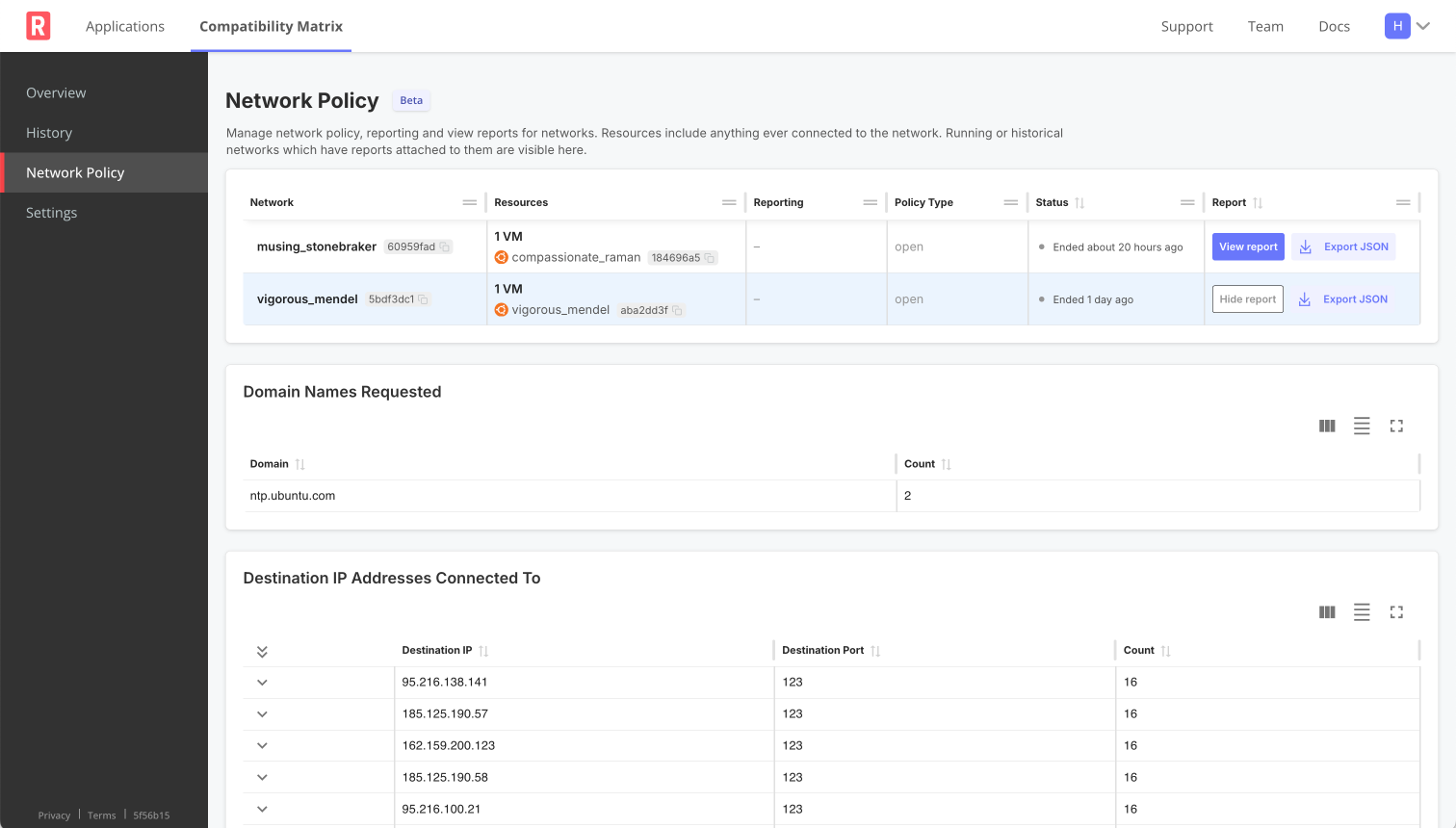
View a larger version of this image
Enable Network Reporting
Networking reporting is not enabled by default. To collect reports, you can enable reporting in the Vendor Portal or with the CLI.
Vendor Portal
To set the network policy and collect and view reports in the Vendor Portal:
-
Go to Compatibility Matrix > Network Policy.
-
To collect a network report, toggle on the switch under Reporting.
-
(Optional) Toggle from
opentoairgapunder Policy Type to block all network egress.
CLI
To collect and view a network report from the CLI:
-
Turn on network reporting:
replicated network update NETWORK_ID --collect-reportWhere
NETWORK_IDis the ID of the network. You can get the network ID by runningreplicated network ls. -
Confirm that Has report is on for the network:
replicated network lsExample output:
ID NAME STATUS CREATED EXPIRES POLICY HAS REPORT
a1b2c3d4 example_network_1 running 2025-01-28 16:04 PST 2025-01-28 18:06 PST open off
e5f6g7h8 example_network_2 running 2025-01-28 12:10 PST 2025-01-28 20:11 PST airgap on -
(Optional) Change the network policy to
airgapto block all network egress.
View Network Reports
After you Enable Network Reporting for a network, you can view network reports.
Vendor Portal
To view network reports in the Vendor Portal:
-
Go to Compatibility Matrix > Network Policy.
-
Where available, click "View report" under Report to see the reporting table. You can also click "Export JSON" to download the raw report data.
noteWhen reporting is on for an active network, all network events display in a Running Report. When the network is terminated, the Report Summary is automatically generated.
CLI
To view network reports from the CLI:
-
Get the network ID:
replicated network ls -
View the network report:
See network event summary that aggregates all unique domains and destination IPs, with connection counts and other details (JSON format):
replicated network report NETWORK_ID --summarySee all network events (JSON format):
replicated network report NETWORK_IDWatch as new network events occur (JSON format):
replicated network report NETWORK_ID --watchnoteNetwork events are batched for display in the report, so appear with a short delay.