Port Forwarding Services with KOTS
This topic describes how to add one or more ports to the Replicated KOTS port forward tunnel by configuring the ports key in the KOTS Application custom resource.
The information in this topic applies to existing cluster installations. For information about exposing services for Replicated kURL or Replicated Embedded Cluster installations, see Exposing Services Using NodePorts.
Overview
For installations into existing clusters, KOTS automatically creates a port forward tunnel and exposes the Admin Console on port 8800 where it can be accessed by users. In addition to the 8800 Admin Console port, you can optionally add one or more extra ports to the port forward tunnel.
Adding ports to the port forward tunnel allows you to port forward application services without needing to manually run the kubectl port-forward command. You can also add a link to the Admin Console dashboard that points to port-forwarded services.
This can be particularly useful when developing and testing KOTS releases for your application, because it provides a quicker way to access an application after installation compared to setting up an ingress controller or adding a load balancer.
Port Forward a Service with the KOTS Application ports Key
To port forward a service with KOTS for existing cluster installations:
-
In a new release, configure the
portskey in the KOTS Application custom resource with details for the target service. For example:apiVersion: kots.io/v1beta1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: my-application
spec:
ports:
- serviceName: my-service
servicePort: 3000
localPort: 8888-
For
ports.serviceName, add the name of the service. KOTS can create a port forward to ClusterIP, NodePort, or LoadBalancer services. For more information about Kubernetes service types, see Service in the Kubernetes documentation. -
For
ports.servicePort, add thecontainerPortof the Pod where the service is running. This is the port where KOTS forwards traffic.noteEnsure that you use the
containerPortand not theservicePort. ThecontainerPortandservicePortare often the same port, though it is possible that they are different. -
For
ports.localPort, add the port to map on the local workstation.
-
-
Promote the release to the channel that you use for internal testing, then install in a development environment to test your changes.
When the application is in a Ready state and the KOTS port forward is running, you will see output similar to the following:
• Press Ctrl+C to exit
• Go to http://localhost:8800 to access the Admin Console
• Go to http://localhost:8888 to access the applicationConfirm that you can access the service at the URL provided in the KOTS CLI output.
-
(Optional) Add a link to the service on the Admin Console dashboard. See Add a Link to a Port-Forwarded Service on the Admin Console Dashboard below.
Add a Link to a Port-Forwarded Service on the Admin Console Dashboard
After you add a service to the KOTS port forward tunnel, you can also optionally add a link to the port-forwarded service on the Admin Console dashboard.
To add a link to a port-forwarded service, add the same URL in the KOTS Application custom resource ports.applicationURL and Kubernetes SIG Application custom resource spec.descriptor.links.url fields. When the URLs in these fields match, KOTS adds a link on the Admin Console dashboard where the given service can be accessed. This process automatically links to the hostname in the browser (where the Admin Console is being accessed) and appends the specified localPort.
To add a link to a port-forwarded service on the Admin Console dashboard:
-
In a new release, open the KOTS Application custom resource and add a URL to the
ports.applicationURLfield. For example:apiVersion: kots.io/v1beta1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: my-application
spec:
ports:
- serviceName: my-service
servicePort: 3000
localPort: 8888
applicationUrl: "http://my-service"Consider the following guidelines for this URL:
- Use HTTP instead of HTTPS unless TLS termination takes place in the application Pod.
- KOTS rewrites the URL with the hostname in the browser during deployment. So, you can use any hostname for the URL, such as the name of the service. For example,
http://my-service.
-
Add a Kubernetes SIG Application custom resource in the release. For example:
# app.k8s.io/v1beta1 Application Custom resource
apiVersion: app.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: "my-application"
spec:
descriptor:
links:
- description: Open App
# url matches ports.applicationURL in the KOTS Application custom resource
url: "http://my-service"-
For
spec.descriptor.links.description, add the link text that will appear on the Admin Console dashboard. For example,Open App. -
For
spec.descriptor.links.url, add the same URL that you used in theports.applicationURLin the KOTS Application custom resource.
-
-
Promote the release to the channel that you use for internal testing, then install in a development environment to test your changes.
When the application is in a Ready state, confirm that you can access the service by clicking the link that appears on the dashboard. For example:
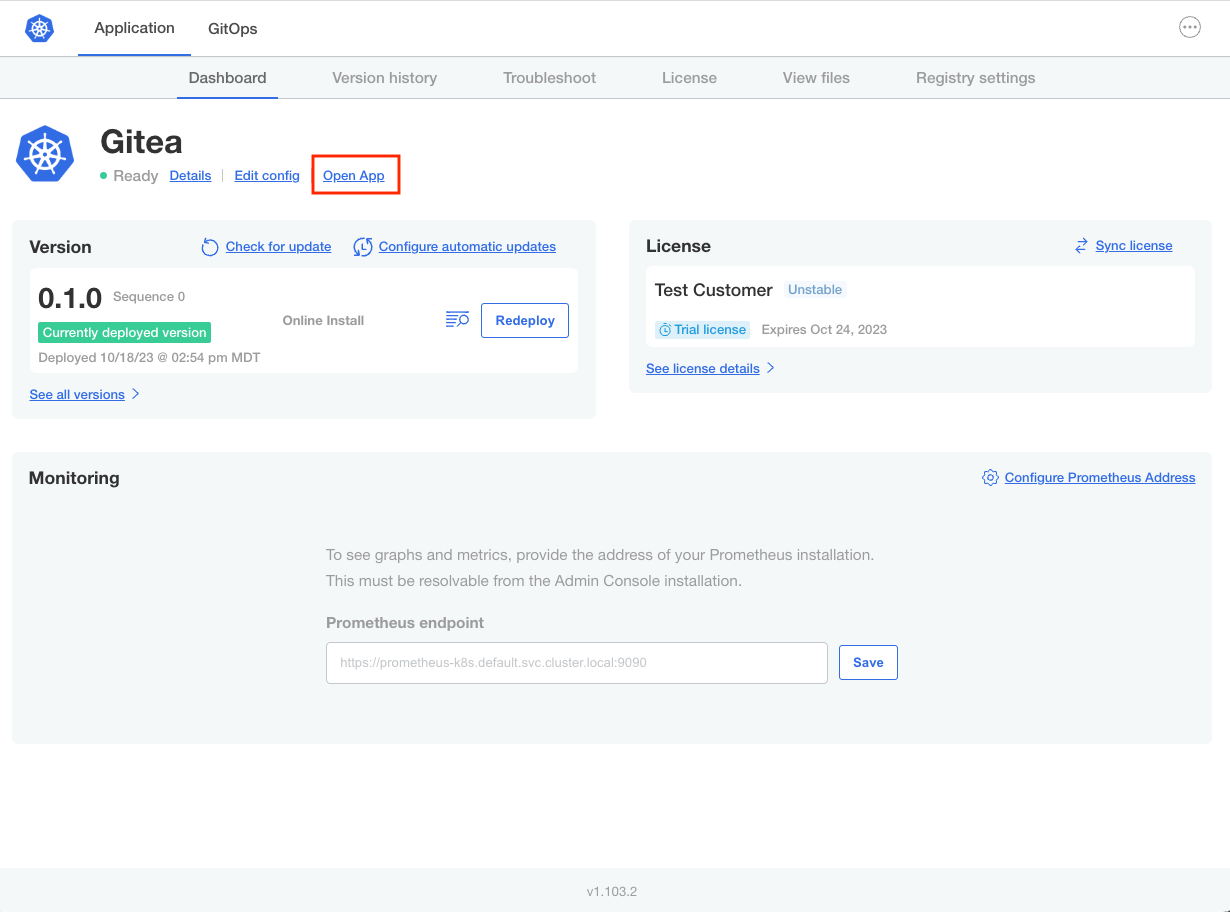
Access Port-Forwarded Services
This section describes how to access port-forwarded services.
Command Line
Run kubectl kots admin-console to open the KOTS port forward tunnel.
The kots admin-console command runs the equivalent of kubectl port-forward svc/myapplication-service <local-port>:<remote-port>, then prints a message with the URLs where the Admin Console and any port-forwarded services can be accessed. For more information about the kubectl port-forward command, see port-forward in the Kubernetes documentation.
For example:
kubectl kots admin-console --namespace gitea
• Press Ctrl+C to exit
• Go to http://localhost:8800 to access the Admin Console
• Go to http://localhost:8888 to access the application
Admin Console
You can optionally add a link to a port-forwarded service from the Admin Console dashboard. This requires additional configuration. For more information, see Add a Link to a Port-Forwarded Service on the Admin Console Dashboard.
The following example shows an Open App link on the dashboard of the Admin Console for an application named Gitea:

View a larger version of this image
Examples
This section provides examples of how to configure the ports key to port-forward a service in existing cluster installations and add links to services on the Admin Console dashboard.
Example: Bitnami Gitea Helm Chart with LoadBalancer Service
This example uses a KOTS Application custom resource and a Kubernetes SIG Application custom resource to configure port forwarding for the Bitnami Gitea Helm chart in existing cluster installations, and add a link to the port-forwarded service on the Admin Console dashboard. To view the Gitea Helm chart source, see bitnami/gitea in GitHub.
To test this example:
-
Pull version 1.0.6 of the Gitea Helm chart from Bitnami:
helm pull oci://registry-1.docker.io/bitnamicharts/gitea --version 1.0.6 -
Add the
gitea-1.0.6.tgzchart archive to a new, empty release in the Vendor Portal along with thekots-app.yaml,k8s-app.yaml, andgitea.yamlfiles provided below. Promote to the channel that you use for internal testing. For more information, see Managing Releases with the Vendor Portal.- kots-app.yaml
- k8s-app.yaml
- gitea.yaml
Description
Based on the templates/svc.yaml and values.yaml files in the Gitea Helm chart, the following KOTS Application custom resource adds port 3000 to the port forward tunnel and maps local port 8888. Port 3000 is the container port of the Pod where the
giteaservice runs.YAML
apiVersion: kots.io/v1beta1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: gitea
spec:
title: Gitea
statusInformers:
- deployment/gitea
ports:
- serviceName: "gitea"
servicePort: 3000
localPort: 8888
applicationUrl: "http://gitea"
icon: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cncf/artwork/master/projects/kubernetes/icon/color/kubernetes-icon-color.pngDescription
The Kubernetes Application custom resource lists the same URL as the
ports.applicationUrlfield in the KOTS Application custom resource ("http://nginx"). This adds a link to the port-forwarded service from the Admin Console dashboard. It also triggers KOTS to rewrite the URL to use the hostname in the browser and append the specifiedlocalPort. The label to be used for the link in the Admin Console is "Open App".YAML
apiVersion: app.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: "gitea"
spec:
descriptor:
links:
- description: Open App
# needs to match applicationUrl in kots-app.yaml
url: "http://gitea"Description
The KOTS HelmChart custom resource provides instructions to KOTS about how to deploy the Helm chart. The
nameandchartVersionlisted in the HelmChart custom resource must match the name and version of a Helm chart archive in the release. Each Helm chart archive in a release requires a unique HelmChart custom resource.YAML
apiVersion: kots.io/v1beta2
kind: HelmChart
metadata:
name: gitea
spec:
# chart identifies a matching chart from a .tgz
chart:
name: gitea
chartVersion: 1.0.6 -
Install the release to confirm that the service was port-forwarded successfully. To test the port forward, click Open App on the Admin Console dashboard after the application reaches a Ready state. For more information, see Online Installation in Existing Clusters with KOTS.
Example: NGINX Application with ClusterIP and NodePort Services
The following example demonstrates how to link to a port-forwarded ClusterIP service for existing cluster installations.
It also shows how to use the ports key to add a link to a NodePort service for kURL installations. Although the primary purpose of the ports key is to port forward services for existing cluster installations, it is also possible to use the ports key so that links to NodePort services for Embedded Cluster or kURL installations use the hostname in the browser. For information about exposing NodePort services for Embedded Cluster or kURL installations, see Exposing Services Using NodePorts.
To test this example:
-
Add the
example-service.yaml,example-deployment.yaml,kots-app.yaml, andk8s-app.yamlfiles provided below to a new, empty release in the Vendor Portal. Promote to the channel that you use for internal testing. For more information, see Managing Releases with the Vendor Portal.- example-service.yaml
- example-deployment.yaml
- kots-app.yaml
- k8s-app.yaml
Description
The YAML below contains ClusterIP and NodePort specifications for a service named
nginx. Each specification uses thekots.io/whenannotation with the Replicated IsKurl template function to conditionally include the service based on the installation type (existing cluster or kURL cluster). For more information, see Conditionally Including or Excluding Resources and IsKurl.As shown below, both the ClusterIP and NodePort
nginxservices are exposed on port 80.YAML
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app: nginx
annotations:
kots.io/when: '{{repl not IsKurl }}'
spec:
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- port: 80
selector:
app: nginx
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app: nginx
annotations:
kots.io/when: '{{repl IsKurl }}'
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 80
nodePort: 8888
selector:
app: nginxDescription
A basic Deployment specification for the NGINX application.
YAML
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
annotations:
backup.velero.io/backup-volumes: nginx-content
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
resources:
limits:
memory: '256Mi'
cpu: '500m'
requests:
memory: '32Mi'
cpu: '100m'Description
The KOTS Application custom resource below adds port 80 to the KOTS port forward tunnel and maps port 8888 on the local machine. The specification also includes
applicationUrl: "http://nginx"so that a link to the service can be added to the Admin Console dashboard.YAML
apiVersion: kots.io/v1beta1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
title: App Name
icon: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cncf/artwork/master/projects/kubernetes/icon/color/kubernetes-icon-color.png
statusInformers:
- deployment/nginx
ports:
- serviceName: "nginx"
servicePort: 80
localPort: 8888
applicationUrl: "http://nginx"Description
The Kubernetes Application custom resource lists the same URL as the
ports.applicationUrlfield in the KOTS Application custom resource ("http://nginx"). This adds a link to the port-forwarded service on the Admin Console dashboard that uses the hostname in the browser and appends the specifiedlocalPort. The label to be used for the link in the Admin Console is "Open App".YAML
apiVersion: app.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: "nginx"
spec:
descriptor:
links:
- description: Open App
# needs to match applicationUrl in kots-app.yaml
url: "http://nginx" -
Install the release into an existing cluster and confirm that the service was port-forwarded successfully by clicking Open App on the Admin Console dashboard. For more information, see Online Installation in Existing Clusters with KOTS.
-
If there is not already a kURL installer promoted to the channel, add a kURL installer to the release to support kURL installs. For more information, see Creating a kURL Installer.
-
Install the release on a VM and confirm that the service was exposed successfully. To test the port forward, click Open App on the Admin Console dashboard after the application reaches a Ready state. For more information, see Online Installation with kURL.
noteEnsure that the VM where you install allows HTTP traffic.